Watch Our Video Rundown
How We Test & Choose
When choosing our recommendations, whether it’s an ultrawide monitor or a budget gaming mouse, we do extensive research first. Being gamers, we only want to bring the best products to your attention, accompanied by accurate information based on real-world testings. This involves several steps to ensure the highest performance standards are met.
Even though the team is already well versed in the latest hardware offerings, the first thing the team does is make sure nothing new is due for release. We want to keep you up-to-date with the latest hardware offerings, especially when it comes to high-end products.
Next, comes benchmarking. We usually do all of our benchmarking in-house; however, if we can’t get our hands on a particular processor, we’ll scour online sources for gaming CPU benchmarks. With benchmarking, we see what CPUs are doing best in each field and how they stack up against each other. This helps ensure that the processors we suggest are rated highly in the gaming category.
It is important to note that we have purchased all the recommended CPUs (plus a few others) for benchmarking, testing, and a bit of gaming, which enables us to create a clearer picture of what truly is the best CPU for gaming.
Check Out The Best CPU Temperature Monitoring Software Here
How does a CPU work?
First off, before running through our best CPU picks, it is important to understand what a CPU is and how it works. This information should help you wrap your head around how a CPU operates, and what you’ll need your new CPU to do in terms of use case, as some are better at certain things than others.
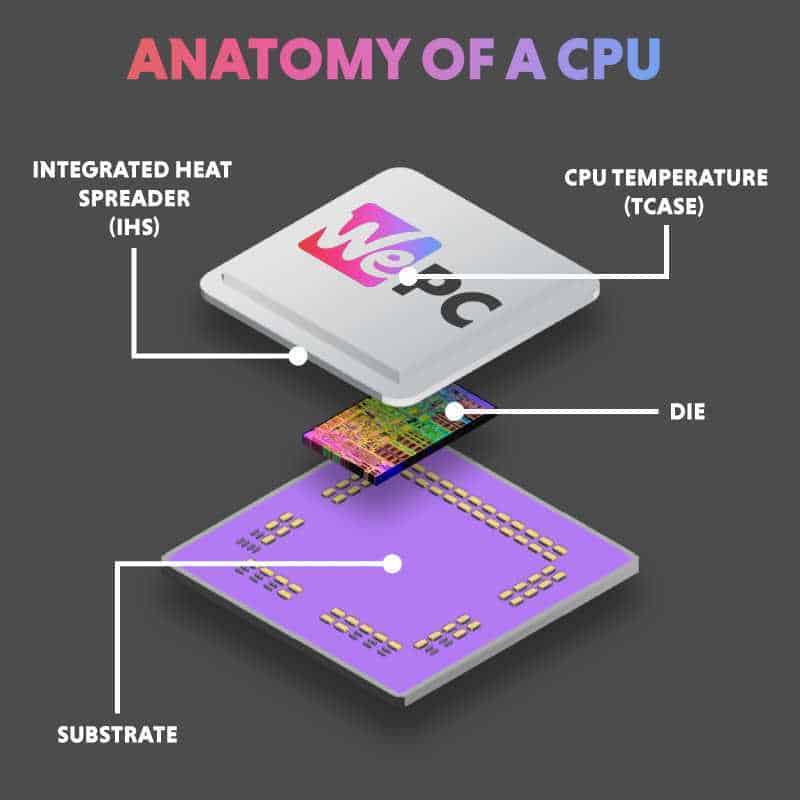
A CPU carries out instructions set by programs. These programs are loaded temporarily into RAM. The information is then moved to cache if it’s important enough. The CPU then makes calculations using its transistors, which are capable of only an on or off output. Using this, the CPU determines a string of ones and zeros – you now have some binary code. This process is broken down into three simple steps: fetch, decode and execute. This is called a cycle and this happens billions of times per second, depending on the clock speed of the processor and the size of the transistors in the CPU.
Here’s the kicker, the process we’ve just run through happens in every CPU, or more notably, every CPU core. Billions of cycles per second are happening at the same time in 64 processing cores if you’re using a Threadripper 3990X, for example.
With that basic understanding out of the way, it’s time to expand on some of the more talked about features of a CPU, such as core count, thread count and clock speed.
Things To Consider
The first thing to consider when choosing your gaming CPU is what you intend to use it for. Just because a CPU is “the best” in one category doesn’t mean it’s the best CPU for you.
But what are you looking for in a CPU? How do you know it’s the one for you? Should it have more cores or faster speeds? Let’s look at a few key factors that may help you decide:
- Casual/ hardcore gaming
- Streaming
- Content creation
- Overclocking

Terms To Know
Choosing a CPU can be daunting for first-time buyers, and there are a few things you should consider before buying one. You wouldn’t want to buy one of AMD’s latest Ryzen chips and find out it isn’t compatible with the rest of your system!
There are a lot of terms that get thrown around in regard to CPUs, so let’s go over some of the most common phrases before breaking down what the best gaming CPU is.
Cores And Threads
A processor is made up of cores and threads. Nowadays, CPUs have multiple cores which allows them to do multiple tasks, think of it as the literal embodiment of the old saying; two heads are better than one.
The computer treats threads as virtual CPUs. The amount of threads is the number of tasks each core can handle. Threads can only do one thing at a time, but they can switch extremely fast. As such, threads serve as an efficient way for your CPU to effectively switch between handling multiple tasks.
Clock Speed
Clock speed, sometimes known as cycle speed, refers to how many cycles a core will perform every second. This is measured in megahertz. So 4MHz would be four million cycles per second.
Processors that are “unlocked” can be overclocked to reach a higher clock speed than their stock speed. However, overclocking has to be done right. If done incorrectly, you might find yourself with a costly paperweight at the end of the day. Nevertheless, it’s a rule of thumb to ask: “Is overclocking worth it?” before doing so.
If you’re unsure which processor you should get, read our article on which CPU do you really need? Or you can check our CPU hierarchy to see a detailed list of CPUs and which category they belong to.
Cores And Clock Speed Combined
Together these will give you a general idea about how well the processor in question will perform, but let’s delve a little deeper. For instance, IPC (instructions per cycle) tells us how many actions can be taken every cycle and is often much harder to find. Moreover, specific tasks utilize fewer cores, like gaming, which means you’ll want strong single-core performance (it’s still good to have at least four cores for gaming, though). On the other hand, tasks such as video rendering utilize a lot of resources, meaning you’ll want extra cores (at least eight +) for a smooth experience.
Ultimately, this is why we always benchmark the CPUs and test processors performing different types of tasks.
IPC and core speed
Core speed is defined by how many cycles per second a CPU can perform. A full CPU cycle is referred to as the instruction cycle, which follows three actions. The actions of the instruction cycle run in the order of fetch, decode and execute – these three actions comprise the instruction cycle.
Not surprisingly, a higher clock speed is superior. However, not all clock speeds are created equal. We will now attempt to simply explain what we mean by this. And, while we leave many components out of the explanation, it serves as a simple enough baseline
Many factors can affect the metrics of clock speed. One of these is the nm process a CPU is built on, which refers to the size of the transistors that make up the logical components of a CPU. There are billions of these microscopic transistors all capable of very simple yes/no outputs, which together equate to more complex logical executions.
7nm transistors are much smaller than 12nm transistors, for example. And this is what we mean when we said not all clock speed is created equal.
Clock speed refers to how many cycles a CPU can perform per second, not how many instructions can be executed per second. This is another measurement known as IPC (instructions per clock).
IPC and clock speed are somewhat intertwined. People are easily fooled into thinking that a CPU with a better clock speed, no matter how old, will always be faster than a new CPU with a lower clock speed. And this simply isn’t true.
Socket Types
The socket is the physical mount on your motherboard that holds the processor in place. As such, the first thing you’re going to want to check is that the socket on your motherboard matches your processor (or vice versa!).
Each brand and (sometimes) line of processors have its own socket type and won’t fit in an alternative one. For example, an AMD Ryzen 7 uses the AM4 socket type and won’t fit into Intel’s LGA 1151 socket.
If you’re purchasing a new CPU and a new motherboard together, check the specs to make sure they’re both the same socket type (I suggest deciding on your processor first, then finding a matching motherboard).
If you’re upgrading one or the other, check the specs online and make sure the new piece of the hardware matches up accordingly.
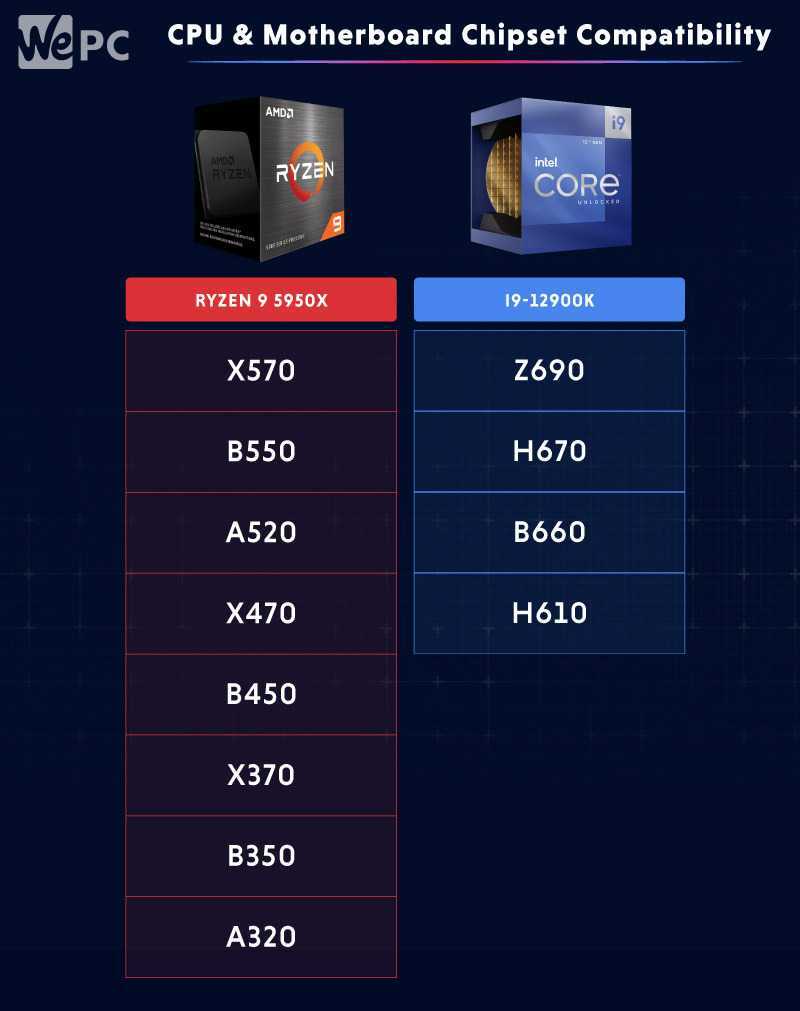
Chipsets
Each processor will have a set of chipsets that it’s compatible with. These chipsets are important when choosing your motherboard, as they determine whether or not some features will be disabled.
The more advanced the chipset, the more features that will be unlocked (More PCIe lanes, more USB 3.1 ports, SATA ports, etc.). As with the socket types, check your hardware specs to see what chipsets are compatible, and what each one will unlock on your board.
For example:
Generation
CPUs come in all shapes and sizes, and one important detail to pay special attention to is their generation. Both AMD and Intel CPU advancements are separated by a generation, for example, the intel i7-11700k is one generation behind the intel i7-12700K.
Why does generation matter? Generation tells you essentially how good a CPU is. Tech-wise, the newest thing on the market is better than the older one, 99% of the time.
Understanding what advancements these generational jumps bring may take a bit of research but are important and a beneficial chunk of information to bring to the table when deciding on a new CPU.
Hardcore Gaming Builds
Sometimes, you want to build a powerful gaming rig. You don’t care about streaming or content creation. Your bottom line is getting those high FPS numbers.
When it comes to a pure gaming build, speed is your friend. Unlike highly taxing programs and tasks, games aren’t as dependant on CPU cores and threads. Anything quad-core or higher is sufficient for gaming.
Most games will run on a dual-core processor, but more and more games are starting to require a quad-core or higher to install and run. That being said, most modern-day CPUs come equipped with at least 4-cores.
For a hardcore gaming build, I would suggest looking for processors that have at least the following speeds:
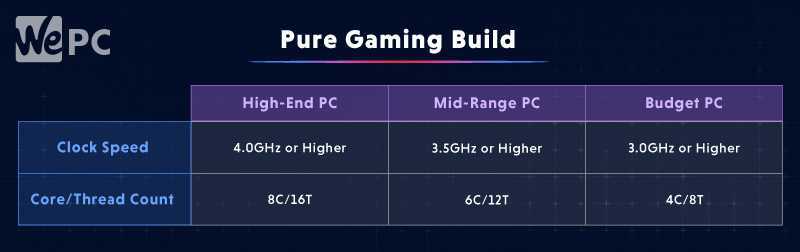
Pairing a fast processor with a good SSD, a powerful graphics card, and some quality RAM will really increase your FPS overall.
Casual Gaming
Maybe you don’t care about high FPS figures or saving your content for the world to see. Perhaps you’re more the casual type, the type who just likes to game now and then in your free time. AAA games titles aren’t really your thing, and you don’t require all that processing power.
If all you’re looking for is a gaming build that will run some low-intensive steam games and esports titles, then a casual gamer setup might be more suited to your needs. Typically, a casual gaming build doesn’t need the latest hardware offerings. It’s also much more affordable than a hardcore gaming build.
When looking for a casual gaming CPU, you should look for one that is at least a quad-core if your budget allows it. It also doesn’t need to be extremely fast.
Let’s see what you should be looking for:
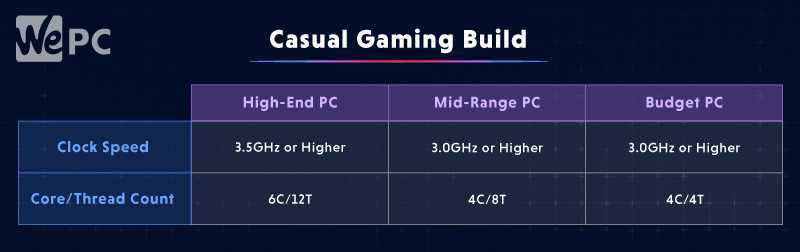
Streaming
A growing trend over the last five years has been to stream and share gaming content. Platforms like YouTube and Twitch are hugely popular amongst the gaming community at the moment, and more people seem to be jumping on the stream build bandwagon. This, however, can be somewhat taxing on your processor if you don’t have a sufficient amount of power.
This means you’re going to need a processor with more cores and threads than your typical hardcore gaming build. Here’s what you should look for if you’re thinking about building a computer for gaming and streaming:
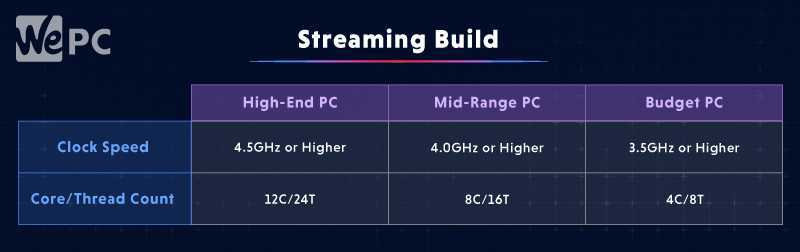
Having a higher core and thread count will help your computer multitask, allowing it to record your game as well as process and everything else that’s going on in the background without the lag.
Content Creation
Let’s say you’ve already got a following on your YouTube channel/ Steam account, and you’re ready to kick production up to the next level and start creating better videos.
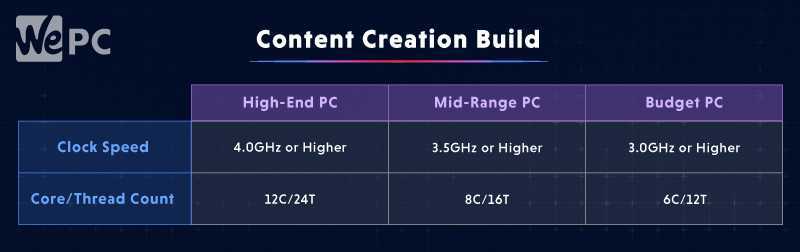
You’ve decided to build a PC that can do it all. It needs to be capable of gaming, streaming and pumping out good quality videos. This is going to require more computing power.
You’re going to need a high core and thread count with fast speeds so that you can render your content as quickly as possible. Here’s what to look for if you want your gaming computer to be an all-round beast:
Overclocking
Technically, all Ryzen CPUs come with overclocking support out of the box but some are better than others – these are the ‘X’ models. You can look at these as the beefed-up versions of the base models and they are all more equipped to handle stronger overclocks.
Ryzen CPUs and the profiles they ship with are incredibly well optimized already, but there is still some performance to be gained out of your Ryzen X in the form of faster RAM.
Without getting too technical, CPU core communication speed in AMD Ryzen processors is directly tied to RAM speed. Pairing your Ryzen processor with a kit of at least 3600Mhz RAM can majorly improve effective overclocks, and even base performance.
This is different for Intel CPUs. Core communication speed in Intel CPUs isn’t directly tied to RAM speed and is the reason Intel processors are not as heavily impacted by slower RAM than Ryzen processors are.
K, KF, KS: Which Is Best For You?
One of the big questions we get asked when referencing Intel CPUs is, what is the difference between K, KF, and KS SKUs? Luckily, the differences between the three are only small, and, nine times out of ten, probably won’t sway your purchasing decision.
Intel’s K CPUs are possibly the most common in this list. The K SKUs simply refer to CPUs that can be overclocked and come with integrated graphics.
KF SKUs are very similar to the K, only KF does not come with any form of integrated graphics. They still have the exact same amount of overclocking potential.
Lastly, we have KS. KS is slightly different, referencing specially selected (binned) CPUs that have much higher overclocking headspace. KS are usually more expensive than the previous SKUs as they house the potential for much greater performance.
Ryzen Or Intel: which Is Better For Gaming?
With AMD making waves in the CPU and GPU industry over the last few years, we often get the question, what’s better for gaming? AMD or Intel? Unfortunately, the answer isn’t as clear cut as it used to be.
If you asked us six years ago when AMD was still rocking the FX series of CPUs, the answer would have been clearly in favour of intel. AMD has since closed the gap and now there’s a large debate among gamers as to what is in fact the best gaming CPU.
Intel definitely has single-core performance won, while AMD takes the win in multicore performance.
Ryzen Or Intel: which is more efficient?
Intel has recently made strides towards CPU efficiency, managing to produce a generation of CPUs more powerful than ever before without containing a full set of performance cores.
When Intel launched the new 12th generation CPUs, it integrated a version of ARM’s LITTLE.big technology into the CPUs. The 12th generation CPUs mark the first desktop processor to include this kind of technology.
LITTLE.big technology works to improve CPU power efficiency, but how does it work exactly?
LITTLE.big technology
Intel’s 12th generation CPUs differ internally from the modern-day desktop CPU you’re used to. The way normal CPUs work is they have any number of identical cores that will take on processing loads indiscriminately. However, LITTLE.big processors have two different kinds of core – P-cores and E-cores.
P-cores represent performance cores, these are the cores clocked at higher speeds that handle all the heavy lifting. E-cores mark efficiency cores and these cores have a lower base clock to be more power-efficient – they’re the cores that handle light usage tasks.
That’s all well and good but how does the CPU know which core to use? Good question. The task of choosing which instruction gets assigned to which core, falls to the Windows kernel scheduler.
The instructions are pre-screened by the scheduler to determine how much processing power they’re going to require, then depending on that the instructions are sent to either a performance or efficiency core.
In-depth Reviews
Here we will take an in-depth look at our best gaming CPUs of 2022.

Intel Core i9-12900K

Boost clock speed (single core)
5.3 GHz
Total Cores / Threads
16/24
P-cores
8
E-cores
8
Socket
LGA 1700
Overclockable
Yes
- Powerful single core performance
- Powerful multi-core performance
- Overclockable
- Expensive
The 12th gen 12900K is the successor to the 11th gen Intel i9-11900K, utilizing the new ‘Alder Lake’ architecture as opposed to the ‘Rocket Lake’ of the older CPU. Unlike the release of Intel’s 11900K, the 12900K has been a huge hit amongst reviewers – despite the more expensive price tag.
The 12900K comes with a 125W TDP which, yes is higher than the AMD counterpart – meaning it does get a little toasty under the hood. The 12900K is only compatible with the new FCLGA1700 socket, meaning a complete upgrade will be necessary if you plan on purchasing this CPU. The new 12900k comes to shelves boasting a core count of 16 and 24 threads, making it a great all-rounder for both multi-tasking and gaming. Intel has put its efforts into architectural improvements with the new Alder Lake lineup, improving on almost every area.
With all these improvements, we finally see Intel regain the top spot as far as gaming is concerned. More impressive, however, is the fact that in workstation and multitasking scenarios, the Intel 12900K is almost as good as the Ryzen 5900X. Pair that with crazy overclocking potential and great single-core performance and you have one tasty processor.
AMD Ryzen 9 5900X

Speed
3.7GHz/ 4.8GHz
Core (Threads)
12/24
Socket
AM4
TDP
105W
- Rivals the Intel i9-10900K in gaming performance
- High multicore performance
- Unlocked overclocking
- More expensive than the Intel alternative
- Requires CPU cooler
It took AMD a while, but finally, they’re at the top of the CPU hierarchy with their extremely impressive Ryzen 9 5900X. This CPU pretty much does it all – gaming performance, overclocking, productivity work, the lot. If you’re looking for the best all-around CPU on the market, look no further – team red has you covered.
The flagship CPU from AMD offers up uncontested gaming performance and fantastic multi-tasking productivity work – all of which are great for gaming, streaming, rendering, and video editing. When you pair that alongside its current price tag, you’d have to say that the 5900X also shows some of the best value in today’s market too.
The 5900X is a 12 core 24 thread part, offering up a 3.7GHz base frequency right out of the box. Furthermore, with PBO, the 5900X can be boosted to 4.8GHz when it needs the additional power most – think gaming or productivity type workflows. AMD, like always, have unlocked the Ryzen 9 5900X for excellent overclocking capabilities, with many users hitting 5.0GHz respectively. This all translates to very good performance in gaming – with single-core performance having the ability to push 100FPS + in the most demanding of modern titles.
The flagship offering also brings excellent future-proofing to your new build, supporting PCIe 4.0 for the next generation of hardware that’s just around the corner. You’ll be able to slot the 5900X into newer 500-series boards alongside older 400-series alternatives, making it not only powerful but versatile too. The only downside is the lack of a cooler – something that AMD’s more budget-oriented alternatives don’ have to worry about.

AMD Ryzen 7 5800X3D

Cores
8
Threads
16
Max boost speed
4.5GHz
L3 Cache
96MB (64MB 3D V-cache)
TDP
105W
- Inexpensive
- Incredible performance
- 3D V-cache
- No cooler
- No native overclocking support
The Ryzen 7 5800X3D is a marvel in CPU engineering, the 5800X3D has technically claimed the top ‘best gaming CPU’ from Intel and their core i9 12900K but there are a couple of reasons it’s not top of our list today. The 5800X3D is an excellent choice for gaming, rocking a cool eight multithreaded CPU cores and a whopping 96MB of brand new AMD 3D V-cache, It seriously gains an edge in some games.
3D V-Cache is where this CPU differed from literally every CPU in the world right now, as it’s the only one to make use of it. 3D cache is not stacked laterally like a normal 2D cache but vertically (thanks to new 3D printing technology) – hence the term 3D cache. This drastically increases the number of chiplets you can cram into an area of any given size, thus resulting in larger cache capacities without sacrificing access speeds. The vertical stacking allows AMD to achieve the massive 96MB L3 cache with a total access speed of 2TB/s in its 5800X3D CPUs.
The 5800X3D has lower core speeds of 3.4GHz base and 4.5GHz max, these speeds are even lower than its brothers the 5800X, the reason for this is the 3D V-cache is unstable at higher core speeds. Thanks to the 5800X3Ds low max core speeds and lack of overclocking support, it’s not very good at single-core workloads or workstation tasks. if ever there was a fully-fledged gaming CPU it would be the 5800X3D.
This new caching technology gives the CPU major advantages in some gaming workloads, but not all. And with the lower core speeds and lack of overclocking support means the 5800X3D is regularly outperformed by cheaper and worse CPUs in scenarios where the cache is not utilised, even in gaming.
For these main reasons, is why the 5800X3D is not higher on our list. You can read the full product review on the Ryzen 7 5800X3D right here.

Intel Core i5-12600KF

Boost clock speed (single core)
4.9 GHz
Total Cores / Threads
10/16
P-cores
6
E-cores
4
Socket
LGA 1700
Overclockable
Yes
- Powerful single core performance
- Amazing multi core performance
- Overclockable
- No in box cooler
- Still more power-hungry than Ryzen
Another of Intel’s latest arrivals comes in the shape of their i5-12600K – their latest mid-range offering. This CPU comes equipped with a much more affordable price tag, but don’t let that fool you, it comes jam-packed with performance, including plenty of overclocking to boot.
The i5-12600K offers up 10 cores and 16 threads, the same as its predecessor the 11900K, but improvements to the architecture bring significant improvements in performance, with up to a 30% increase in FPS on some titles. Although AMD’s 5600X still beats the card in multi-core tests, making it the better CPU in this price range for workstation uses. On top of this, the 12600K typically (though not in all cases) beats the 5600X in single-core and gaming scenarios.
This performance is thanks to the impressive 3.7Hz base clock speed of the 12600K, with a tasty max single-core boost frequency of 4.9GHz. If you’re into overclocking, there’s also a ton of potential to be had by doing so with this chip. Pushing it up to 5.3GHz is not out of the question, putting it right up there with the likes of the 10900K, but be aware you will need a pricey cooling rig to do so. Even pre-overclocking the 12600K runs hot, which is the only real drawback of this chip, and this does necessitate slightly more being spent on cooling, eating into the savings somewhat.
Nevertheless, assuming you have an FCLGA1700 socket motherboard (the chipset is not backwards compatible) you won’t go far wrong picking this processor for your gaming rig. Overall, as far as gaming is concerned, at this price range, you’ll struggle to find anything that can match the 12600K’s performance. A fantastic CPU from Intel.
AMD Ryzen 5 5600X

Speed
3.7GHz/ 4.6GHz
Core (Threads)
6/12
Socket
AM4
TDP
65W
- Set to out-perform the 10600K
- Great value for money
- Unlocked overclocking
- Slightly more expensive than what we’re used to from AMDs midrange offering
- Requires CPU cooler
The 5600X was one of the most anticipated CPUs to be released when Ryzen announced their 5000 series CPU lineup – mainly thanks to some impressive benchmarking rumours. It came to the table offering a shocking mix of Intel-beating value and performance in both gaming and workflow scenarios. If you’re looking for a well-priced CPU that can smash out AAA game titles at over 100fps and has excellent multi-tasking abilities, the 5600X should be high on your list of recommendations. It’s the very reason why it finds itself in our list of best CPUs for gaming.
Price/performance, this chip is one of the best we’ve seen in a long time. It has a base clock speed of 4.1GHz alongside a 4.8GHz boost clock frequency – putting it next to some of the top performers in this guide. Furthermore, with a 19% increase in IPC, this thing really does leave the last generation of 3000 series CPUs in the dust. It comes with its own CPU cooling fan which AMD says is newly designed with excellent efficiency and almost no noise output – a feature the premium CPU options in AMD’s 5000 series lineup can’t boast.
Overall, whilst the 11600K offers better single-core performance at a cheaper RRP, the 5600X is still one of the best CPUs you can get at this respective price point.
AMD Ryzen 9 5950X

Speed
3.4GHz/ 4.9GHz
Core (Threads)
16/32
Socket
AM4
TDP
105W
- Very high single-core performance
- Great for gaming and workstation tasks
- Excellent overclocking potential
- High price tag
- Requires CPU cooler
From a gaming standpoint, the Ryzen 9 5950X isn’t quite as good as the 5900x or 10900K. That being said, it still offers very good performance and actually outperforms them both when it comes to multi-tasking type workflows.
The 5950X is another step in the HEDT direction for desktop CPUs – offering up 16 cores and 32 threads for truly unparalleled workstation performance in this guide. Unlike HEDT though, you won’t have to purchase a custom board to run this bad boy, it’ll slot right into your AM4 motherboard without a hitch.
In terms of raw gaming performance, the 5950X does show a decent account of itself in this guide. Whilst it’s not as good as the 10900K or 5950X, it still offers very stable FPS figures when playing modern AAA titles. With a base clock frequency of 3.4GHz and a boost up to 4.9GHz, you’ll have more than enough juice to drive the most intense rendering and multi-tasking workflows.
All being said, this is an excellent all-around CPU – but mainly tailored towards the individual that really needs that extra productivity performance. Gamers will be better suited toward fewer cores and higher single-core performance.
Final Word
Choosing the best CPU for gaming can be a fun and rewarding experience, but it can also be a challenge. Now that you’re familiar with the best gaming CPUs of 2020, it should hopefully make an informed decision when it comes to buying a lot easier. Don’t forget to pick the right cooling solution for your CPU to ensure it runs at optimal levels at all times!
Deciding which gaming CPU you’re going to get will come down to what your personal needs are going to be. Using this article should help you decide which one is best for you.








Where the F is ryzen 7?😂
Hi Yumil, the page needs a massive update.
The fastest 6&8 cores CPUs for 2019 are the 8086K and 9900KS
Both are Intel fastest factory Coffeelake and Coffeelake Refresh CPUs.
Both Intel 8086K and 9900KS are faster than the AMD 3600X and 3800X
9900KS is the last upgrade for the 300 series boards.
May I suggest the AMD Ryzen 5 2600X for the best budget gaming CPU? More threads than the Intel Core i5-9600K and the price is waaay better. Great guide nevertheless
Hi Irakleitos,
We have updated the builds since your comment, take a look and let us know what you think!
Nice job on a very good guide.
However, may I suggest one correction: In the section “Terms to Know”, subsection “Clock Speed”, sentence “So 4MHz would be 4 billion cycles per second.”, the word “billion” should be “million”.
Thanks for the correction champted
Hey. I sent a screenshot. Did you get it?
Not sure we did friend. What was it regarding?