Today we’re looking at the 5600 vs 12400 CPUs and asking, which is better? AMD recently released the 5600 alongside two other CPUs. and we’re looking to see how it stacks up against Intel’s incredibly efficient and budget-friendly 12400, since they’re available in the same budget. Will the AMD or Intel CPU prevail in this AMD Ryzen 5600 vs Core i5 12400 article?
If you want to learn more about AM5 or Zen 4, we have articles on those. Or for team Intel, maybe our ‘best 12th gen motherboard article‘ will suit you better.

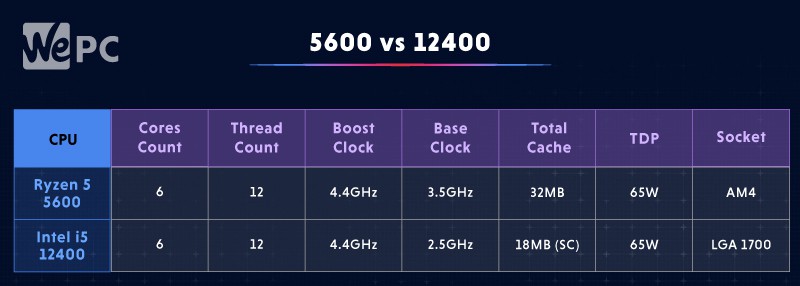
5600 vs 12400: Specifications
When comparing any two PC components it’s important to analyse the on-paper specifications, as doing so will help us to gain an understanding of how they both work and how they will perform against each other. Some examples of CPU specifications would be core count, clock speed and cache size.
Ryzen 5 5600
The Ryzen 5 5600 is the newest release on today’s list debuting on April 4 2022. This is a budget-friendly CPU and performs well in terms of specifications at this price point. It’s set to be the predecessor to the Ryzen 5 3600 and it outperforms it significantly.
The specifications of the Ryzen 5 5600 are as follows:
- 6 cores
- 12 threads
- Boost clock 4.4GHz
- Base clock 3.5GHz
- L1 cache 384KB
- L2 cache 3MB
- L3 cache 32MB
- Default TDP 65W
- Socket AM4
Core i5 12400
The i5 12400 is a staple in the budget market, and offering insane performance for less than $200 is the name of the game. Releasing in Q1 2022, it’s taken the market by storm ever since, but can it beat the 5600?
- 6 cores
- 12 threads
- Boost clock 4.4GHz
- Base clock 2.5GHz
- L2 cache 7.5MB
- L3 cache 16MB (Smart Cache)
- Default TDP 65W
- Socket LGA 1700
5600 vs 12400: specification comparison
We will now compare the on-paper specifications of each of our CPUs and determine how well they stack up against each other. Doing so should help us gain a deeper knowledge and understanding of how these chips function and what they bring to the table.
Core count
Both CPUs on our list today have the same core count.

If your CPU has a higher core count, it means your CPU will be better at multitasking natively. This is all thanks to the CPU having a higher number of cores, that can each process instructions independently of each other. Most modern applications support multicore CPU usage but some older software packages do not, so your CPU may not be to blame if you find an older application chugging a little bit.
Thread count
Both CPUs on today’s list have the same number of threads.

Thread count is different to core count but ultimately achieves the same goal. CPU cores are given the ability to process two instructions simultaneously through a technology called multithreading. Threads are the name given to the second instruction a CPU core processes.
A greater number of threads increase performance in multicore workloads by about 65%, and this makes the base CPU cores so much more efficient. But cores and threads are not the same – threads are not physical like CPU cores.
CPU cores occupy physical space on the CPU die. Threads, on the other hand, are virtualised and have to share resources with CPU cores, making them slightly slower as a result.
Core speeds
Both CPUs on today’s list have the same boost speeds, but the 5600 has a higher base speed.

Core speeds are the measure of how many cycles your CPU can complete in a second – these ‘cycles’ refer to the CPU instruction cycle. The instruction cycle is comprised of three main actions: fetch, decode and execute. These are the actions that fundamentally comprise processing as we know it.
Generally, when speaking of CPUs in the same generation, it’s safe to compare core speeds and determine the faster CPU as the one with the highest core speed and similar/more core and thread counts. Since both of the CPUs on our list today have the same core and thread count, it’s safe to say the 5600 takes the win for the higher base speed.
Cache
The 5600 has more cache capacity than the 12400

A CPU’s cache is an extension of system RAM, constructed close to CPU cores to facilitate fast access speeds. The cache acts as a buffer to feed CPU cores instructions from RAM- the faster the cache the faster it can feed CPU cores instructions. Modern-day CPUs are constructed with three cache levels in mind.
Cache is split into three levels and they follow alphanumerical order.
- L1
- L2
- L3
Level one cache is the cache located close to the CPU cores and has the greatest access speeds but also the smallest capacity. This is the level reserved for only the most vital data
Level two cache is a middle ground between level one and level three cache, with median capacity and median speed, reserved for your less vital data,
Level three cache is where most of your regularly accessed data is stored, such as programs and file paths. This has a very large capacity in comparison to the other two levels of cache but is also much slower.
TDP
Both CPUs today have the same TDP.

TDP stands for thermal design power and is the maximum amount of thermal energy a component can output under normal operating conditions. TDP is essentially heat and heat needs to be negated in order to ensure proper operation. A CPU’s TDP can be indicative of a higher performance CPU as power is synonymous with a high TDP.
It’s important to have a cooler capable of negating and dissipating the TDP generated by your CPU, check inside your cooler manual if you’re unsure how high a TDP your cooler can handle.
Since both of our CPUs are capable of overclocking, it’s important to leave enough thermal headroom in your system. This is because overclocking increases a component’s TDP exponentially due to the expected workload and higher voltages.
Socket
The Ryzen 5 5600 belongs to the AM4 socket and the 12400 belongs to the LGA 1700 socket.
A CPU socket is just the component of a motherboard that the CPU is seated in. Every CPU has a socket and it’s important you take into account the socket the CPU belongs to and buy the motherboard that corresponds to that CPU socket.
Integrated graphics
The intel core i5 12400 is the only CPU with integrated graphics.

Most Intel CPUs contain integrated graphics of some sort unless they are the ‘F’ or ‘KF’ version of the CPU, which tends to be a little cheaper.
The specifications of Intel’s UHD 730 graphics are as follows:
- GPU base frequency: 300MHz
- GPU Max dynamic frequency: 1.45GHz
- Execution units: 24
- Max resolution (HDMI): 4096 x 2160 @ 60Hz
- Max resolution (DP): 7680 x 4320 @ 60Hz
- DirectX support: 12
- OpenGL support: 4.5
- Number of supported displays: 4
The Intel UHD 730 graphics chip contained within the 12400 is a great mid-range option, Intel integrated graphics can’t really hold a candle to the likes of Ryzens 5700G though. But the 5600 we have here doesn’t have any iGPU at all. There is a 5600G however if you’re interested.
iGPUs can be a great choice if you’re strapped for cash and need a quick solution to obtaining both a CPU and GPU in one little package. However, CPUs with integrated graphics tend to be les powerful than their non-iGPU counterparts, due to the precious CPU die real estate the iGPU occupies. This leaves less room for CPU components.
5600 vs 12400 benchmarks
We’ll populate this as soon as we have in-house data, all deductions we have made are based on third party data for now.
Price
The Core i5 12400 is much cheaper than the 5600.

The core i5 12400 is looking like a pretty serious contender, not only does it perform slightly better than the 12400 it’s also cheaper.
The average price online for the i5 12400 is around $170, that’s a cost per core of $28, whereas the 5600 just launched for $199, that’s a cost per core of $33.
Despite this, if you’re interested in picking up a Ryzen 5 5600, you can check out our Ryzen 5 5600 where to buy page.
AMD Ryzen 5600 vs Core i5 12400: Conclusion

The i5 12400 takes the win here for us, and the 5% better performance coupled with the cheaper price is well worth the purchase, not to mention the fact that the 12400 is capable of working with DDR5 RAM, improving its speed further. The 5600 does not have this feature as the AM4 platform is solely limited to DDR4.
We think the 5600 came a little too late, as AM5 is just around the corner and it’s going to render AM4 without any significant upgrades. AM4 has reached the end, whereas the 12400 remains strong on LGA 1700, which will also play host to the next generation of Intel CPUs (13th Gen). This means there’s a clear upgrade path in the future.
You can save even more money by picking up the 12400F, without the integrated graphics portion if you already have a discrete GPU. We hope this AMD Ryzen 5600 vs Core i5 12400 article helped you make a decision when considering your next CPU.

